I have recently contributed to a proof of concept study published in the prestigious Nature Communication Journal (doi:10.1038/s41467-018-03931-4) [1]. The study involved collaborations with experimental groups across the University of Lincoln (UoL), the University of Molise (Italy) and the Royal Holloway University of London, coordinated by Dr Enrico Ferrari (UoL).
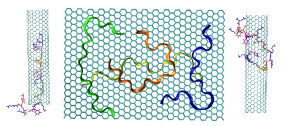
The motivation for this is that, generally, the high diversity of protein properties necessitates the development of unique nanoparticle bio-conjugation methods optimized for each protein. Enrico had the brilliant idea to design a universal bio-conjugation approach that uses a new recombinant fusion protein combining two distinct domains. For this purpose, the N-terminal part is Glutathione S-Transferase (GST, a protein ubiquitously present in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes with the ability to catalyze the conjugation of the reduced form of glutathione (GSH) to xenobiotic substrates for the purpose of detoxification) from Schistosoma japonicum was bound covalently bound to gold nanoparticles (GNPs) by gold-sulfur bonds. The C-terminal part of this multi-domain construct is the SpyCatcher from Streptococcus pyogenes, which can capture recombinant proteins encoding a SpyTag (see Figure 1).

Figure 1: Crystal structure of the SpyCatcher/SpyTag complex (PDB code: 4MLI). The image was created using the Chimera software.
In this work, it was shown that Spy-Catcher can be immobilized covalently on GNPs through GST without the loss of its full functionality. We then show that GST-SpyCatcher-activated particles can covalently bind a SpyTag-modified protein by simple mixing through the spontaneous formation of an unusual isopeptide bond.
In this paper, Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations have been used to study the absorption of the protein on the surface of the gold nanoparticles coated with citrate molecules. The nanoparticle surface is approximated in the simulation as a flat gold surface. An atomistic simulation of the entire particle would be challenging since the NP used in the experimental study (~40 nm in diameter) is too large (only the NP would consist of 2 million atoms, see Figure 2).
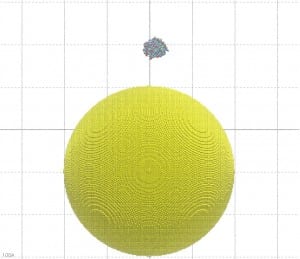
Figure 2: A 40 nm particle compared to the size of the GST protein. If not differently indicated, all the pictures on this blog have been generated using the VMD software.
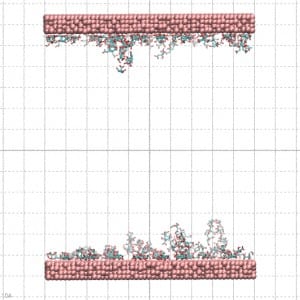
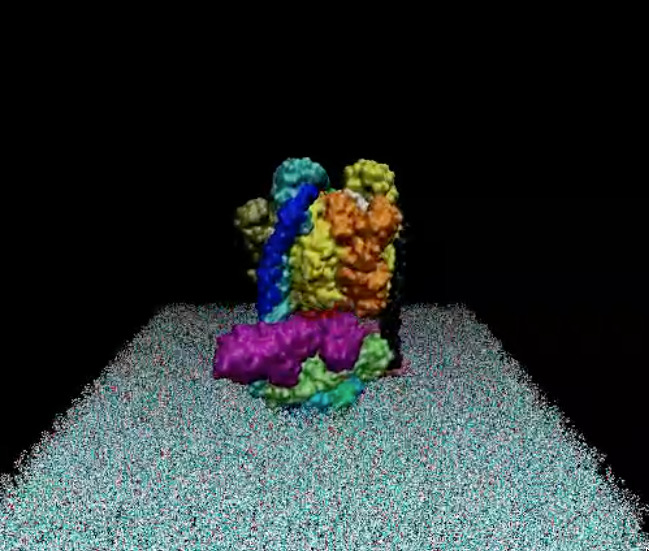
Gold nanoparticles are quickly produced by reducing gold salts in a citrate solution whose concentration determines the nanoparticle’s diameter. The citrate molecules absorbed on the nanoparticle surface negatively charge it. To reproduce this effect, the gold surface used for the MD simulation was prepared by letting citrate molecules be absorbed into it. In this way, the citrate molecules in the complex with Na counterions coat the gold surface as a molecular quill (see Figure 3)!
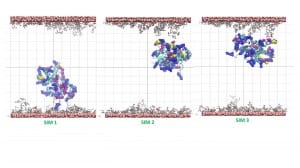
The simulation result clearly indicates the protein’s tendency to bind the coated layer driven by electrostatic interactions with the negative carboxylates of the citrate with the side chain of the arginine residues on the protein surface. Figure 4 shows conformations of the protein bonded to the layer at the end of three 20 ns simulations starting from different velocities. The results support the experimental finding on the possible mechanism of protein absorption on the nanoparticles.
REFERENCE
- Ma, A. Saccardo, D. Roccatano, D. Aboagye-Mensah, M. Alkaseem, M. Jewkes, F. Di Nezza, M. Baron, M. Soloviev, E. Ferrari. Modular assembly of proteins on nanoparticles. Nature Communication.9, 1489 (2018).