In my recent public talk at the Gravity Fields Festival 2016, I have shown several models of molecular machines, I have added some of them to this blog with the details on their construction.
The models have been generated using a small script in awk language and represented using the program VMD (http://www.ks.uiuc.edu/Research/vmd/).
The Photosynthetic Apparatus of Rhodospirillum photometricum
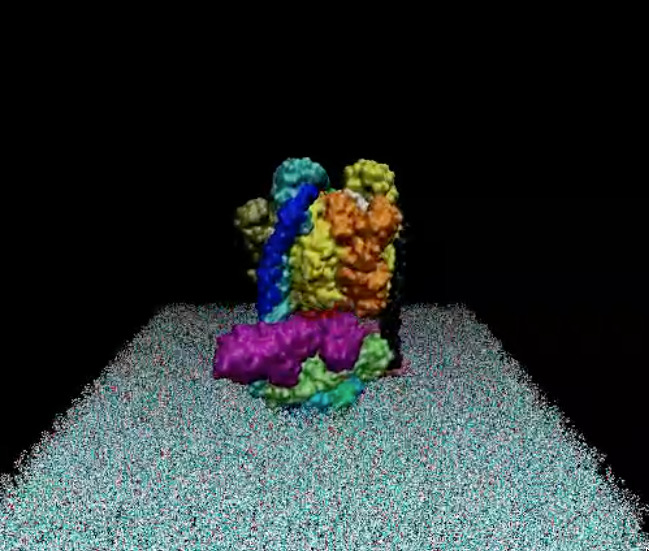
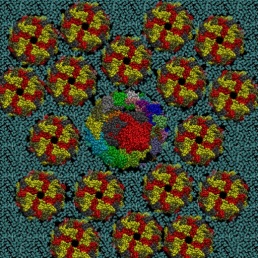
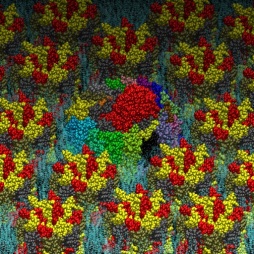
The photosynthetic apparatus of purple photosynthetic bacteria is particularly simple and it is located in a specialized membrane system that develops in the bacterial cytoplasm. They are composed of four integral membrane protein complexes: a peripheral LH2 antennae complexes that serve to collect light and transfer the absorbed energy to the second complex, the core-complex, which is constituted of an antenna complex (LH1) associated with the photochemical reaction center (RC). The LH1 serves to funnel the light energy to the RC where a charge separation takes place catalyzing the oxidation of a water soluble carrier. The different crystallographic structures of these components are available in the Protein Data Bank. Based on the supramolecular assembly of these proteins observed using Atomic Force Topographic (Scheuring et al. 2007), it was possible to generate a molecular model of the photosynthetic apparatus of Rsp. photometricum. The model comprises one RC-LH1 core complex surrounded by several LH2 complexes. The model is a chimera of crystallographic structures from different organism. In particular, for the LH2 was used the nonameric Rps. acidophila structure [PDB id: 1KZU (McDermott et al., 1995)].
The LH1-RC complex is based on the recent crystal structure from Thermochromatium tedium [PDB id: 4V8K (Niwa et al. Nature, 2014)]. LH2 and the core complex were first centered and aligned and then translated and rotated to their relative positions using as reference the AFM topography reported by in Scheuring et al. 2007. A DPPC lipid bilayer was also generated using the tools in the VMD program and added to the model by removing the lipid molecules overlapping with the proteins.
Two views of the model are reported below. The complete fly-by animation is here.
The Yeast V-ATPase
Vacuolar-ATPase (V-ATPase) is an ancient enzyme with remarkably diverse functions in eukaryotic organisms. It is used to acidify different organelles and as a proton pump across the plasma membranes of numerous cell types. For its functions, V-ATPases use the energy produced by ATP hydrolysis. It is generally seen as the polar opposite of ATP Synthase that uses the energy from a proton gradient to produce ATP.
The structure of the model of the Yeast V-ATPase was generated by Zhao et al. using electron microscopy add homology modeling (PDB Id: 3J9U, Zhao et al. Nature, 2015). I have just generated a DPPC lipid bilayer using the tools in the VMD program and just added to the model by removing the lipid molecules overlapping with the proteins.
A view of the model is reported below. The complete fly-by animation is here.